AWS Machine Learning
-
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 5 hours, 4 minutes ago
How Tines enhances security analysis with Amazon Quick Suite
 Organizations face challenges in quickly detecting and responding to user account […]
Organizations face challenges in quickly detecting and responding to user account […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 5 hours, 5 minutes ago
How Lendi revamped the refinance journey for its customers using agentic AI in 16 weeks using Amazon Bedrock
 This post was co-written with Davesh […]
This post was co-written with Davesh […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 5 hours, 5 minutes ago
Building a scalable virtual try-on solution using Amazon Nova on AWS: part 1
 In this first post in a two-part series, we examine how retailers can […]
In this first post in a two-part series, we examine how retailers can […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 day, 5 hours ago
Build safe generative AI applications like a Pro: Best Practices with Amazon Bedrock Guardrails
 Are you struggling to balance generative AI safety […]
Are you struggling to balance generative AI safety […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 day, 5 hours ago
Build a serverless conversational AI agent using Claude with LangGraph and managed MLflow on Amazon SageMaker AI
 Customer service teams face a […]
Customer service teams face a […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 day, 5 hours ago
Building specialized AI without sacrificing intelligence: Nova Forge data mixing in action
 Large language models (LLMs) perform well on general tasks […]
Large language models (LLMs) perform well on general tasks […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 5 days, 5 hours ago
Large model inference container – latest capabilities and performance enhancements
 Modern large language model (LLM) deployments face an escalating […]
Modern large language model (LLM) deployments face an escalating […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 5 days, 5 hours ago
Reinforcement fine-tuning for Amazon Nova: Teaching AI through feedback
 Foundation models deliver impressive out-of-the-box performance for general […]
Foundation models deliver impressive out-of-the-box performance for general […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 5 days, 5 hours ago
Learnings from COBOL modernization in the real world
 There’s a lot of excitement right now about AI enabling mainframe application modernization. B […]
There’s a lot of excitement right now about AI enabling mainframe application modernization. B […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 6 days, 6 hours ago
Building intelligent event agents using Amazon Bedrock AgentCore and Amazon Bedrock Knowledge Bases
 Large conferences and events generate […]
Large conferences and events generate […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 6 days, 6 hours ago
Efficiently serve dozens of fine-tuned models with vLLM on Amazon SageMaker AI and Amazon Bedrock
 Organizations and individuals running multiple […]
Organizations and individuals running multiple […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 week ago
-
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 week ago
Global cross-Region inference for latest Anthropic Claude Opus, Sonnet and Haiku models on Amazon Bedrock in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, and Taiwan
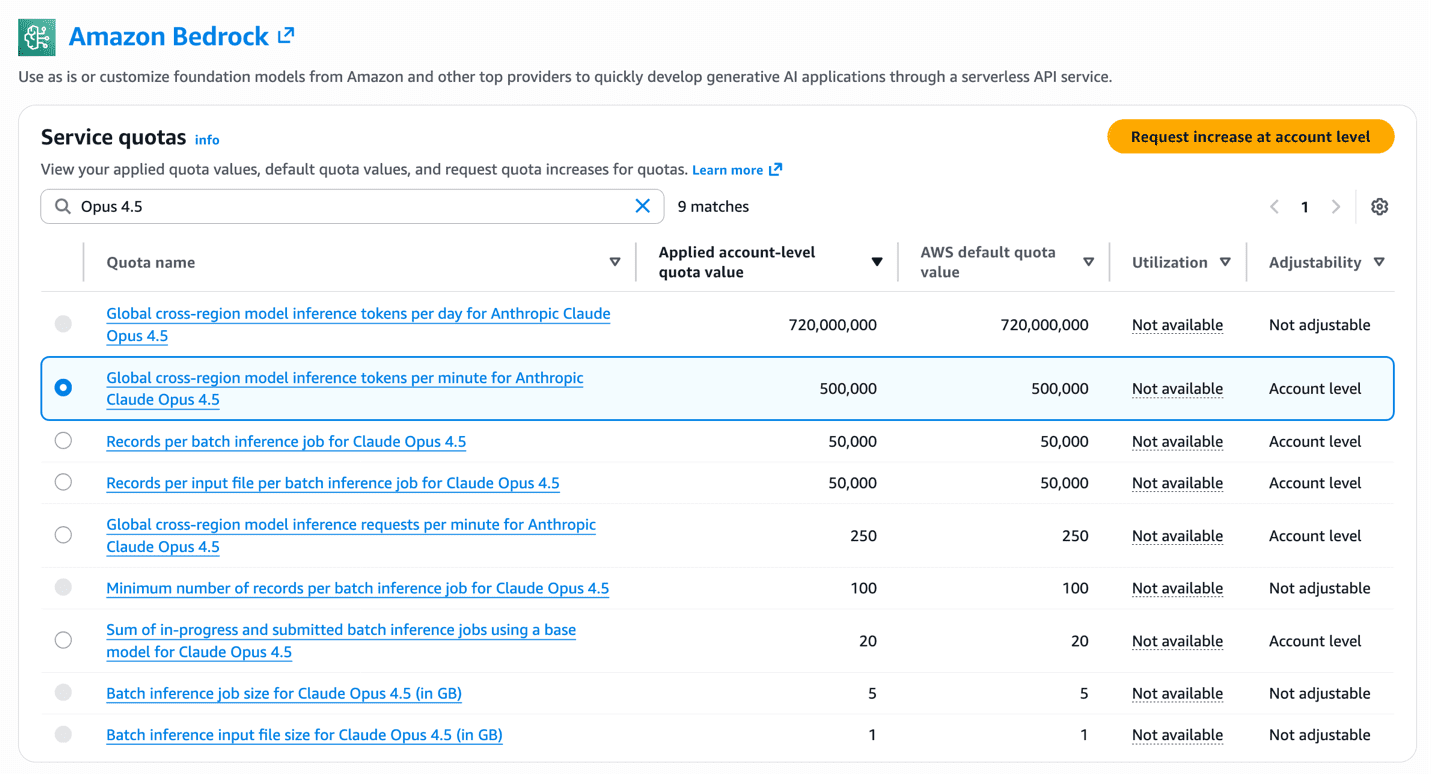
 Organizations across in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, and Taiwan can now access Anthropic Claude Opus 4.6, Sonnet 4.6, and Claude Haiku 4.5 through Global cross-Region inference (CRIS) on Amazon Bedrock—delivering foundation models through a globally distributed inference architecture designed for scale. Global CRIS offers three key advantages: higher quotas, cost efficiency, and intelligent request routing to inference capacity across AWS commercial Regions for enabling AI use-cases like chatbots, autonomous coding agents, and financial analysis systems for customers. In this post, we are exciting to announce availability of Global CRIS for customers in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, and Taiwan and give a walkthrough of technical implementation steps, and cover quota management best practices to maximize the value of your AI Inference deployments. We also provide guidance on best practices for production deployments. Global cross Region inference CRIS is a powerful Amazon Bedrock capability that organizations can use to seamlessly distribute inference processing across multiple AWS Regions. This capability helps you achieve higher throughput while building at scale, helping to make sure your generative AI applications remain responsive and reliable even under heavy load. You access CRIS through inference profiles, which operate on two key concepts: Source Region – The Region from which you make the API request Destination Region – A Region to which Amazon Bedrock can route the request for inference CRIS operates through the secure AWS network with end-to-end encryption for both data in transit and at rest. When you submit an inference request from a source Region, CRIS intelligently routes the request to one of the destination Regions configured for the inference profile over the Amazon Bedrock managed network. The inference request travels over the AWS global network by Bedrock and responses are returned to your application in the source Region. The key distinction is that while inference processing (the transient computation) might occur in another Region, the data at rest—including logs, knowledge bases, and stored configurations—remains exclusively within your source Region. Amazon Bedrock provides two types of cross-Region inference profiles: Geographic CRIS (which routes within a specific geography such as US, EU, APAC, Australia, Japan) and Global CRIS (which routes to supported commercial Regions worldwide). Customers in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia can now access Claude Opus 4.6, Sonnet 4.6, and Haiku 4.5 through Global CRIS, which routes requests across Regions for higher throughput and built-in resilience during traffic spikes. Why Global CRIS for Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia As organizations shift from conversational AI assistants to autonomous agents that plan, execute, and coordinate complex workflows, production AI deployments require more resilient and scalable infrastructure. Global CRIS delivers Claude Opus 4.6, Sonnet 4.6 and Haiku 4.5 through a high availability architecture designed to meet the demands of this shift to production-scale autonomous systems. As autonomous agents increasingly handle merchant operations, coordinate logistics networks, and automate financial workflows across use-cases for customers in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia, infrastructure reliability directly impacts the continuity of these autonomous decision-making systems. Global CRIS routes inference requests across more inference capacity on AWS Regions worldwide, reducing the likelihood that your applications experience service throttling during traffic spikes. This routing capability delivers built-in resilience, allowing your agentic applications to maintain operational continuity even as demand patterns shift. Source Regions configuration in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia At launch, customers in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia can call Global CRIS profiles from the following source Regions: Source Region AWS Commercial Regions Availability Global CRIS routing Asia Pacific (Singapore) ap-southeast-1 Available now Routes to more than 20 supported AWS commercial Regions globally Asia Pacific (Jakarta) ap-southeast-3 Available now Routes to more than 20 supported AWS commercial Regions globally Asia Pacific (Taipei) ap-east-2 Available now Routes to more than 20 supported AWS commercial Regions globally Asia Pacific (Thailand) ap-southeast-7 Available now Routes to more than 20 supported AWS commercial Regions globally Asia Pacific (Malaysia) ap-southeast-5 Available now Routes to more than 20 supported AWS commercial Regions globally Once invoked behind the scenes, Global CRIS will manage routing of requests to any supported commercial AWS Regions. Prerequisites Before using Global CRIS, you need to configure IAM permissions that enable cross-Region routing for your inference requests. Configure IAM permissions Before you can invoke Claude models through Global CRIS, you must configure IAM permissions that account for the cross-Region routing architecture. The following section walks through the policy structure and explains why three separate statements are required. Complete the following steps to configure IAM permissions for Global CRIS. The IAM policy grants permission to invoke Claude models through Global CRIS. The policy requires three statements because CRIS routes requests across Regions: you call the inference profile in your source Region (Singapore or Jakarta), which then invokes the foundation model in whichever destination Region CRIS selects. The third statement uses “aws:RequestedRegion”: “unspecified” to grant the necessary permissions for Global CRIS to route your requests across Regions. Replace with your AWS account ID and adjust the source Region if using Jakarta (ap-southeast-3) instead of Singapore (ap-southeast-1). { “Version”: “2012-10-17”, “Statement”: [ { “Sid”: “GrantGlobalCrisInferenceProfileRegionAccess”, “Effect”: “Allow”, “Action”: “bedrock:InvokeModel”, “Resource”: [ “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0” ], “Condition”: { “StringEquals”: { “aws:RequestedRegion”: “ap-southeast-1” } } }, { “Sid”: “GrantGlobalCrisInferenceProfileInRegionModelAccess”, “Effect”: “Allow”, “Action”: “bedrock:InvokeModel”, “Resource”: [ “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0” ], “Condition”: { “StringEquals”: { “aws:RequestedRegion”: “ap-southeast-1”, “bedrock:InferenceProfileArn”: [ “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0” ] } } }, { “Sid”: “GrantGlobalCrisInferenceProfileGlobalModelAccess”, “Effect”: “Allow”, “Action”: “bedrock:InvokeModel”, “Resource”: [ “arn:aws:bedrock:::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”, “arn:aws:bedrock:::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0”, “arn:aws:bedrock:::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0” ], “Condition”: { “StringEquals”: { “aws:RequestedRegion”: “unspecified”, “bedrock:InferenceProfileArn”: [ “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0” ] } } } ] } It’s important to note that if your organization’s service control policies (SCPs) deny access to unspecified Regions, Global CRIS will not function. We recommend validating your SCP configuration before deploying production workloads that depend on global routing. If your organization restricts AWS API calls to specific Regions, make sure your SCP includes “unspecified” in the approved Regions list. The following example shows how to configure an SCP that permits Global CRIS routing. Add your source Region for Global CRIS (Singapore ap-southeast-1 or Jakarta ap-southeast-3) along with other Regions your organization uses: { “Version”: “2012-10-17”, “Statement”: [ { “Sid”: “DenyAllOutsideApprovedRegions”, “Effect”: “Deny”, “Action”: “*”, “Resource”: “*”, “Condition”: { “StringNotEquals”: { “aws:RequestedRegion”: [ “ap-southeast-1”, “unspecified” ] } } } ] } With IAM permissions configured, you can start invoking Claude models through Global CRIS using inference profiles and the Converse API. Use cross-Region inference profiles Global inference profiles are identified by the global. prefix in their model identifier—a naming convention that you can use to distinguish global routing profiles from Regional or single-Region model IDs. Use these inference profile IDs when making API calls instead of the standard model IDs: Model Base model ID Global inference profile ID Claude Sonnet 4.6 anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-6 global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-6 Claude Opus 4.6 anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1 global.anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1 Claude Sonnet 4.5 anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0 global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0 Claude Haiku 4.5 anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0 global.anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0 Both the InvokeModel and Converse APIs support cross-Region inference profiles. We recommend using the Converse API—this approach provides a simplified interface and consistent request/response format across different foundation models, so you can switch between models without rewriting integration code. Make your first API call Getting started with Global CRIS requires only a few changes to your existing application code. The following code snippet demonstrates how to invoke Claude Opus 4.6 using Global CRIS in Python with the boto3 SDK: import logging import os import boto3 from botocore.exceptions import ClientError # Configure logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) # Load configuration from environment variables with defaults REGION = os.getenv( “AWS_REGION”, “ap-southeast-1” ) # Singapore or Jakarta (ap-southeast-3) MODEL_ID = os.getenv(“MODEL_ID”, “global.anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”) MAX_TOKENS = int(os.getenv(“MAX_TOKENS”, “8000”)) TEMPERATURE = float(os.getenv(“TEMPERATURE”, “1”)) THINKING_TYPE = os.getenv(“THINKING_TYPE”, “adaptive”) EFFORT_LEVEL = os.getenv(“EFFORT_LEVEL”, “medium”) # Initialize Bedrock Runtime client for your Region bedrock_runtime = boto3.client(service_name=”bedrock-runtime”, region_name=REGION) # Example: Architecture trade-offs analysis user_query = “Analyze the trade-offs between microservices and monolithic architectures for a mid-size SaaS company.” # Make inference request using Converse API with adaptive thinking try: response = bedrock_runtime.converse( modelId=MODEL_ID, messages=[{“role”: “user”, “content”: [{“text”: user_query}]}], inferenceConfig={“maxTokens”: MAX_TOKENS, “temperature”: TEMPERATURE}, additionalModelRequestFields={ “thinking”: {“type”: THINKING_TYPE}, “output_config”: {“effort”: EFFORT_LEVEL}, }, ) except ClientError as e: logger.error(“Failed to invoke model %s: %s”, MODEL_ID, e) raise # Extract response content output_message = response[“output”][“message”] has_thinking = any(block.get(“type”) == “thinking” for block in output_message[“content”]) logger.info(“Effort level: %s”, EFFORT_LEVEL) logger.info(“Claude decided to think: %s”, has_thinking) for block in output_message[“content”]: if block.get(“type”) == “thinking”: thinking_tokens = len(block[“thinking”].split()) logger.info(“[Thinking]: ~%d words”, thinking_tokens) elif block.get(“text”): logger.info(“[Response]: %s”, block[“text”]) If this is your first time working with a cross-Region capability, you might expect that routing requests to multiple Regions would complicate your monitoring setup. With Global CRIS, that’s not the case. Your Amazon CloudWatch metrics, CloudWatch logs, and AWS CloudTrail audit logs remain in your source Region, even when inference requests are processed elsewhere. Your existing dashboards, alarms, and audit trail continue to work exactly as they do today. For more information on the Converse API and available parameters, see the Amazon Bedrock API Reference. Building on this foundation, let’s explore quota management strategies to make sure your deployment can scale with demand. Quota management As your application scales from prototype to production, understanding and managing service quotas becomes critical for maintaining consistent performance. This section covers how quotas work, how to monitor your usage, and how to request increases when needed. The following figure shows the Amazon Bedrock Service Quotas page in the AWS console, where you can view your applied account-level quota values for Global CRIS inference profiles. Understanding quotas and planning for scale Understanding quotas and planning for scale is the first step in making sure your Global CRIS deployment can handle production traffic without throttling. Amazon Bedrock enforces service quotas to facilitate fair resource allocation and system stability. This consideration becomes critical as your application scales from prototype to production. For Global CRIS, quotas are measured in two dimensions, each serving a distinct purpose in capacity management: Tokens per minute (TPM) – The maximum number of tokens (input + output) that can be processed per minute Requests per minute (RPM) – The maximum number of inference requests that can be made per minute Default quotas vary by model and are allocated per source Region. You can view your current quotas in the AWS Service Quotas console by navigating to Amazon Bedrock service quotas in your source Region (Singapore or Jakarta). Be advised that Amazon Bedrock uses a token burndown rate that weighs output tokens more heavily than input tokens when calculating quota consumption. The burndown rate is 5:1—output tokens consume five times more quota than input tokens because generating tokens requires more computation than processing input. Quota consumption = Input tokens + (Output tokens × 5) For example, if your request uses 10,000 input tokens and generates 5,000 output tokens: Total quota consumption = 10,000 + (5,000 × 5) = 35,000 tokens The request consumes 35,000 tokens against your TPM quota for throttling purposes. When planning capacity requirements and requesting quota increases, you need to account for this burndown rate in your calculations. If your application processes requests with this same token pattern at 100 requests per minute, the total quota consumption would be 3,500,000 TPM (100 requests × 35,000 tokens per request). When working with your AWS Account Manager on quota increase requests, provide your expected request volume, average input tokens per request, and average output tokens per request so they can calculate the appropriate quota allocation using this burndown multiplier. Managing quotas effectively We recommend setting up CloudWatch alarms at 70–80% quota utilization to request increases before hitting throttling limits. The CloudWatch metrics InputTokenCount and OutputTokenCount track your consumption in real-time, while the InvocationClientErrors metric indicates throttling when it spikes—providing early warning signals for capacity planning. For detailed guidance on available metrics and how to configure monitoring for your Bedrock workloads, refer to Monitoring the performance of Amazon Bedrock. For non-time-sensitive workloads, Claude Haiku 4.5 supports batch inference at 50% cost savings. Batch requests process asynchronously within 24 hours and don’t count against your real-time TPM quota. Requesting quota increases Consider the following factors when determining whether you need quota increases: workload scale (requests per minute during peak traffic), output token ratio (high output generation consumes quota faster), and growth projections (account for 6–12 month scaling needs). If your workload requires quotas beyond the default limits, you can request increases through the AWS Service Quotas console. Complete the following steps to request quota increases through the AWS Service Quotas console: Sign in to the AWS Management Console for AWS Service Quotas in your source Region. Navigate to AWS services and select Amazon Bedrock. Search for Global cross-Region model inference tokens per minute for your specific model. Select the quota and choose Request increase at account level. Enter your desired quota value with justification for the increase. Submit the request for AWS review. Plan ahead when requesting quota increases to help ensure capacity is available before your launch or scaling events. For large-scale deployments or time-sensitive launches, we recommend working with your AWS account team to help ensure appropriate capacity planning and expedited review. With quota management strategies in place, let’s explore how to choose between Opus 4.6, Sonnet 4.6 and Haiku 4.5 for your specific use cases. Migrating from Claude 3.x to Claude 4.5 / 4.6 The migration from Claude 3.x to Claude 4.5 / 4.6 represents a substantial technological leap for organizations using either Opus, Sonnet or Haiku versions. Claude’s hybrid reasoning architecture introduces substantial improvements in tool integration, memory management, and context processing capabilities. For more technical implementation guidance, see the AWS blog post, Migrate from Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 3.x to Claude Sonnet 4.x on Amazon Bedrock, which provides essential best practices that are also valid for the migration to the new Claude Sonnet 4.6 model. Additionally, Anthropic’s migration documentation offers model-specific optimization strategies and considerations for transitioning to Claude 4.5 / 4.6 models. Best practices Consider the following optimization techniques to maximize performance and minimize costs for your workloads: 1. Prompt caching for repeated context Prompt caching delivers up to 90% cost reduction on cached tokens and up to 85% latency improvement for workloads that repeatedly use the same context. Cache system prompts exceeding 500 tokens, documentation content, few-shot examples, and tool definitions. Structure prompts with static content first, followed by dynamic queries. See Prompt caching for faster model inference User Guide for implementation details. 2. Model selection strategy Consider task complexity, latency requirements, cost constraints, and accuracy needs when choosing between models. We recommend Claude Opus 4.6 for the most complex tasks requiring frontier intelligence, such as complex multi-step reasoning, sophisticated autonomous agents, and precision-critical analysis. Claude Sonnet 4.6 is well suited for complex problems requiring agent planning and execution. Claude Haiku 4.5 delivers near-frontier performance at lower cost, making it optimal for high-volume operations and latency-sensitive experiences. For multi-agent architectures, consider using Opus 4.6 or Sonnet 4.6 as orchestrator and Haiku 4.5 for parallel execution workers. 3. Adaptive and extended thinking for complex tasks Claude Opus 4.6 supports adaptive thinking, an evolution of extended thinking that gives Claude the freedom to think if and when it determines reasoning is required. You can guide how much thinking Claude allocates using the effort parameter, optimizing both performance and speed. Sonnet 4.6 and Haiku 4.5 support extended thinking, where the model generates intermediate reasoning steps through problem decomposition, self-correction, and exploring multiple solution paths. These thinking capabilities deliver accuracy improvements on complex reasoning tasks, so enable them selectively where accuracy improvements justify the additional quota usage. 4. Load testing for quota validation Run load tests before production launch to measure actual quota consumption under peak traffic. Configure your test client with adaptive retry mode (Config(retries={‘mode’: ‘adaptive’})) to handle throttling during the test, use tools like Locust or boto3 with threading to simulate concurrent requests, and monitor the CloudWatch metrics during your load test to observe TPM and RPM consumption patterns. A test with 20 concurrent threads making continuous requests will quickly reveal whether your quota allocation matches your expected load. Summary and next steps Global cross-Region inference on Amazon Bedrock delivers Claude Opus 4.6, Sonnet 4.6, and Haiku 4.5 models to organizations in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia with two key advantages: cost savings compared to Regional profiles, and intelligent routing across more than 20 AWS Regions for maximum availability and scale. This infrastructure enables production AI applications across Southeast Asia, from real-time customer service to financial analysis and autonomous coding assistants. Claude Opus 4.6 provides intelligence for the most demanding enterprise workloads, Sonnet 4.6 delivers balanced performance for daily production use cases, and Haiku 4.5 enables cost-efficient high-volume operations. For multi-agent architectures, combine these models to optimize for both quality and economics. We encourage you to get started today with Global cross-Region inference in your applications. Complete the following steps to begin: Sign in to the Amazon Bedrock console in any of the source Regions listed above, e.g. Singapore (ap-southeast-1) or Jakarta (ap-southeast-3). Configure IAM permissions using the policy template provided in this post. Make your first API call using the global inference profile ID. Implement prompt caching for cost savings on repeated context. For more information: Amazon Bedrock Documentation Cross-Region inference User Guide Amazon Bedrock pricing Anthropic Claude Documentation Get started with Amazon Bedrock About the Authors Traci Lim Traci Lim is a Senior AI/ML Specialist Technical Account Manager at AWS based in Singapore. A machine learning engineer by trade, he works with startups and enterprises to operationalize and scale AI/ML applications in production, with a focus on GenAIOps, Agentic Ops, operational excellence, and cost and performance optimization. Prior to AWS, Traci led engineering teams in the tech and financial industries, scaling distributed AI systems across AWS, Azure, GCP, and SAP. He is a builder at heart, always looking for ways to create meaningful impact through technology. Vincent Wang Vincent Wang serves as a GenAI Specialist Solutions Architect at AWS, based in Sydney, Australia. Drawing on more than 8 years of experience in cloud computing, he plays a key role in designing and consulting on modern cloud-native architectures that enable customers to harness the power of AI and machine learning for their businesses. His areas of expertise include AI, Agentic AI, and open source software. Chanmi EUN Chanmi EUN is a Senior Go-to-Market Specialist for Generative AI at Amazon Web Services in Singapore, where she drives adoption of cutting-edge AI technologies among startup customers. She crafts strategic initiatives, develops impactful sales plays, and orchestrates partnerships to accelerate generative AI adoption across the Asia-Pacific Region. Drawing on rich experience in the tech industry, Chanmi seamlessly combines deep expertise with her multilingual capabilities to deliver transformative results in the rapidly evolving AI landscape. Melanie Li Melanie Li, PhD, is a Senior Generative AI Specialist Solutions Architect at AWS based in Sydney, Australia, where her focus is on working with customers to build solutions using state-of-the-art AI/ML tools. She has been actively involved in multiple generative AI initiatives across APJ, harnessing the power of LLMs. Prior to joining AWS, Dr. Li held data science roles in the financial and retail industries. Saurabh Trikande Saurabh Trikande is a Senior Product Manager for Amazon Bedrock and Amazon SageMaker Inference. He is passionate about working with customers and partners, motivated by the goal of democratizing AI. He focuses on core challenges related to deploying complex AI applications, inference with multi-tenant models, cost optimizations, and making the deployment of generative AI models more accessible. In his spare time, Saurabh enjoys hiking, learning about innovative technologies, following TechCrunch, and spending time with his family. Sharadha Kandasubramanian Sharadha Kandasubramanian is a Senior Technical Program Manager for Amazon Bedrock. She drives cross-functional GenAI programs for Amazon Bedrock, enabling customers to grow and scale their GenAI workloads. Outside of work, she’s an avid runner and biker who loves spending time o […]
Organizations across in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, and Taiwan can now access Anthropic Claude Opus 4.6, Sonnet 4.6, and Claude Haiku 4.5 through Global cross-Region inference (CRIS) on Amazon Bedrock—delivering foundation models through a globally distributed inference architecture designed for scale. Global CRIS offers three key advantages: higher quotas, cost efficiency, and intelligent request routing to inference capacity across AWS commercial Regions for enabling AI use-cases like chatbots, autonomous coding agents, and financial analysis systems for customers. In this post, we are exciting to announce availability of Global CRIS for customers in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, and Taiwan and give a walkthrough of technical implementation steps, and cover quota management best practices to maximize the value of your AI Inference deployments. We also provide guidance on best practices for production deployments. Global cross Region inference CRIS is a powerful Amazon Bedrock capability that organizations can use to seamlessly distribute inference processing across multiple AWS Regions. This capability helps you achieve higher throughput while building at scale, helping to make sure your generative AI applications remain responsive and reliable even under heavy load. You access CRIS through inference profiles, which operate on two key concepts: Source Region – The Region from which you make the API request Destination Region – A Region to which Amazon Bedrock can route the request for inference CRIS operates through the secure AWS network with end-to-end encryption for both data in transit and at rest. When you submit an inference request from a source Region, CRIS intelligently routes the request to one of the destination Regions configured for the inference profile over the Amazon Bedrock managed network. The inference request travels over the AWS global network by Bedrock and responses are returned to your application in the source Region. The key distinction is that while inference processing (the transient computation) might occur in another Region, the data at rest—including logs, knowledge bases, and stored configurations—remains exclusively within your source Region. Amazon Bedrock provides two types of cross-Region inference profiles: Geographic CRIS (which routes within a specific geography such as US, EU, APAC, Australia, Japan) and Global CRIS (which routes to supported commercial Regions worldwide). Customers in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia can now access Claude Opus 4.6, Sonnet 4.6, and Haiku 4.5 through Global CRIS, which routes requests across Regions for higher throughput and built-in resilience during traffic spikes. Why Global CRIS for Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia As organizations shift from conversational AI assistants to autonomous agents that plan, execute, and coordinate complex workflows, production AI deployments require more resilient and scalable infrastructure. Global CRIS delivers Claude Opus 4.6, Sonnet 4.6 and Haiku 4.5 through a high availability architecture designed to meet the demands of this shift to production-scale autonomous systems. As autonomous agents increasingly handle merchant operations, coordinate logistics networks, and automate financial workflows across use-cases for customers in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia, infrastructure reliability directly impacts the continuity of these autonomous decision-making systems. Global CRIS routes inference requests across more inference capacity on AWS Regions worldwide, reducing the likelihood that your applications experience service throttling during traffic spikes. This routing capability delivers built-in resilience, allowing your agentic applications to maintain operational continuity even as demand patterns shift. Source Regions configuration in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia At launch, customers in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia can call Global CRIS profiles from the following source Regions: Source Region AWS Commercial Regions Availability Global CRIS routing Asia Pacific (Singapore) ap-southeast-1 Available now Routes to more than 20 supported AWS commercial Regions globally Asia Pacific (Jakarta) ap-southeast-3 Available now Routes to more than 20 supported AWS commercial Regions globally Asia Pacific (Taipei) ap-east-2 Available now Routes to more than 20 supported AWS commercial Regions globally Asia Pacific (Thailand) ap-southeast-7 Available now Routes to more than 20 supported AWS commercial Regions globally Asia Pacific (Malaysia) ap-southeast-5 Available now Routes to more than 20 supported AWS commercial Regions globally Once invoked behind the scenes, Global CRIS will manage routing of requests to any supported commercial AWS Regions. Prerequisites Before using Global CRIS, you need to configure IAM permissions that enable cross-Region routing for your inference requests. Configure IAM permissions Before you can invoke Claude models through Global CRIS, you must configure IAM permissions that account for the cross-Region routing architecture. The following section walks through the policy structure and explains why three separate statements are required. Complete the following steps to configure IAM permissions for Global CRIS. The IAM policy grants permission to invoke Claude models through Global CRIS. The policy requires three statements because CRIS routes requests across Regions: you call the inference profile in your source Region (Singapore or Jakarta), which then invokes the foundation model in whichever destination Region CRIS selects. The third statement uses “aws:RequestedRegion”: “unspecified” to grant the necessary permissions for Global CRIS to route your requests across Regions. Replace with your AWS account ID and adjust the source Region if using Jakarta (ap-southeast-3) instead of Singapore (ap-southeast-1). { “Version”: “2012-10-17”, “Statement”: [ { “Sid”: “GrantGlobalCrisInferenceProfileRegionAccess”, “Effect”: “Allow”, “Action”: “bedrock:InvokeModel”, “Resource”: [ “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0” ], “Condition”: { “StringEquals”: { “aws:RequestedRegion”: “ap-southeast-1” } } }, { “Sid”: “GrantGlobalCrisInferenceProfileInRegionModelAccess”, “Effect”: “Allow”, “Action”: “bedrock:InvokeModel”, “Resource”: [ “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0” ], “Condition”: { “StringEquals”: { “aws:RequestedRegion”: “ap-southeast-1”, “bedrock:InferenceProfileArn”: [ “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0” ] } } }, { “Sid”: “GrantGlobalCrisInferenceProfileGlobalModelAccess”, “Effect”: “Allow”, “Action”: “bedrock:InvokeModel”, “Resource”: [ “arn:aws:bedrock:::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”, “arn:aws:bedrock:::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0”, “arn:aws:bedrock:::foundation-model/anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0” ], “Condition”: { “StringEquals”: { “aws:RequestedRegion”: “unspecified”, “bedrock:InferenceProfileArn”: [ “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0”, “arn:aws:bedrock:ap-southeast-1::inference-profile/global.anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0” ] } } } ] } It’s important to note that if your organization’s service control policies (SCPs) deny access to unspecified Regions, Global CRIS will not function. We recommend validating your SCP configuration before deploying production workloads that depend on global routing. If your organization restricts AWS API calls to specific Regions, make sure your SCP includes “unspecified” in the approved Regions list. The following example shows how to configure an SCP that permits Global CRIS routing. Add your source Region for Global CRIS (Singapore ap-southeast-1 or Jakarta ap-southeast-3) along with other Regions your organization uses: { “Version”: “2012-10-17”, “Statement”: [ { “Sid”: “DenyAllOutsideApprovedRegions”, “Effect”: “Deny”, “Action”: “*”, “Resource”: “*”, “Condition”: { “StringNotEquals”: { “aws:RequestedRegion”: [ “ap-southeast-1”, “unspecified” ] } } } ] } With IAM permissions configured, you can start invoking Claude models through Global CRIS using inference profiles and the Converse API. Use cross-Region inference profiles Global inference profiles are identified by the global. prefix in their model identifier—a naming convention that you can use to distinguish global routing profiles from Regional or single-Region model IDs. Use these inference profile IDs when making API calls instead of the standard model IDs: Model Base model ID Global inference profile ID Claude Sonnet 4.6 anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-6 global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-6 Claude Opus 4.6 anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1 global.anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1 Claude Sonnet 4.5 anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0 global.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0 Claude Haiku 4.5 anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0 global.anthropic.claude-haiku-4-5-20251001-v1:0 Both the InvokeModel and Converse APIs support cross-Region inference profiles. We recommend using the Converse API—this approach provides a simplified interface and consistent request/response format across different foundation models, so you can switch between models without rewriting integration code. Make your first API call Getting started with Global CRIS requires only a few changes to your existing application code. The following code snippet demonstrates how to invoke Claude Opus 4.6 using Global CRIS in Python with the boto3 SDK: import logging import os import boto3 from botocore.exceptions import ClientError # Configure logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO) logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) # Load configuration from environment variables with defaults REGION = os.getenv( “AWS_REGION”, “ap-southeast-1” ) # Singapore or Jakarta (ap-southeast-3) MODEL_ID = os.getenv(“MODEL_ID”, “global.anthropic.claude-opus-4-6-v1”) MAX_TOKENS = int(os.getenv(“MAX_TOKENS”, “8000”)) TEMPERATURE = float(os.getenv(“TEMPERATURE”, “1”)) THINKING_TYPE = os.getenv(“THINKING_TYPE”, “adaptive”) EFFORT_LEVEL = os.getenv(“EFFORT_LEVEL”, “medium”) # Initialize Bedrock Runtime client for your Region bedrock_runtime = boto3.client(service_name=”bedrock-runtime”, region_name=REGION) # Example: Architecture trade-offs analysis user_query = “Analyze the trade-offs between microservices and monolithic architectures for a mid-size SaaS company.” # Make inference request using Converse API with adaptive thinking try: response = bedrock_runtime.converse( modelId=MODEL_ID, messages=[{“role”: “user”, “content”: [{“text”: user_query}]}], inferenceConfig={“maxTokens”: MAX_TOKENS, “temperature”: TEMPERATURE}, additionalModelRequestFields={ “thinking”: {“type”: THINKING_TYPE}, “output_config”: {“effort”: EFFORT_LEVEL}, }, ) except ClientError as e: logger.error(“Failed to invoke model %s: %s”, MODEL_ID, e) raise # Extract response content output_message = response[“output”][“message”] has_thinking = any(block.get(“type”) == “thinking” for block in output_message[“content”]) logger.info(“Effort level: %s”, EFFORT_LEVEL) logger.info(“Claude decided to think: %s”, has_thinking) for block in output_message[“content”]: if block.get(“type”) == “thinking”: thinking_tokens = len(block[“thinking”].split()) logger.info(“[Thinking]: ~%d words”, thinking_tokens) elif block.get(“text”): logger.info(“[Response]: %s”, block[“text”]) If this is your first time working with a cross-Region capability, you might expect that routing requests to multiple Regions would complicate your monitoring setup. With Global CRIS, that’s not the case. Your Amazon CloudWatch metrics, CloudWatch logs, and AWS CloudTrail audit logs remain in your source Region, even when inference requests are processed elsewhere. Your existing dashboards, alarms, and audit trail continue to work exactly as they do today. For more information on the Converse API and available parameters, see the Amazon Bedrock API Reference. Building on this foundation, let’s explore quota management strategies to make sure your deployment can scale with demand. Quota management As your application scales from prototype to production, understanding and managing service quotas becomes critical for maintaining consistent performance. This section covers how quotas work, how to monitor your usage, and how to request increases when needed. The following figure shows the Amazon Bedrock Service Quotas page in the AWS console, where you can view your applied account-level quota values for Global CRIS inference profiles. Understanding quotas and planning for scale Understanding quotas and planning for scale is the first step in making sure your Global CRIS deployment can handle production traffic without throttling. Amazon Bedrock enforces service quotas to facilitate fair resource allocation and system stability. This consideration becomes critical as your application scales from prototype to production. For Global CRIS, quotas are measured in two dimensions, each serving a distinct purpose in capacity management: Tokens per minute (TPM) – The maximum number of tokens (input + output) that can be processed per minute Requests per minute (RPM) – The maximum number of inference requests that can be made per minute Default quotas vary by model and are allocated per source Region. You can view your current quotas in the AWS Service Quotas console by navigating to Amazon Bedrock service quotas in your source Region (Singapore or Jakarta). Be advised that Amazon Bedrock uses a token burndown rate that weighs output tokens more heavily than input tokens when calculating quota consumption. The burndown rate is 5:1—output tokens consume five times more quota than input tokens because generating tokens requires more computation than processing input. Quota consumption = Input tokens + (Output tokens × 5) For example, if your request uses 10,000 input tokens and generates 5,000 output tokens: Total quota consumption = 10,000 + (5,000 × 5) = 35,000 tokens The request consumes 35,000 tokens against your TPM quota for throttling purposes. When planning capacity requirements and requesting quota increases, you need to account for this burndown rate in your calculations. If your application processes requests with this same token pattern at 100 requests per minute, the total quota consumption would be 3,500,000 TPM (100 requests × 35,000 tokens per request). When working with your AWS Account Manager on quota increase requests, provide your expected request volume, average input tokens per request, and average output tokens per request so they can calculate the appropriate quota allocation using this burndown multiplier. Managing quotas effectively We recommend setting up CloudWatch alarms at 70–80% quota utilization to request increases before hitting throttling limits. The CloudWatch metrics InputTokenCount and OutputTokenCount track your consumption in real-time, while the InvocationClientErrors metric indicates throttling when it spikes—providing early warning signals for capacity planning. For detailed guidance on available metrics and how to configure monitoring for your Bedrock workloads, refer to Monitoring the performance of Amazon Bedrock. For non-time-sensitive workloads, Claude Haiku 4.5 supports batch inference at 50% cost savings. Batch requests process asynchronously within 24 hours and don’t count against your real-time TPM quota. Requesting quota increases Consider the following factors when determining whether you need quota increases: workload scale (requests per minute during peak traffic), output token ratio (high output generation consumes quota faster), and growth projections (account for 6–12 month scaling needs). If your workload requires quotas beyond the default limits, you can request increases through the AWS Service Quotas console. Complete the following steps to request quota increases through the AWS Service Quotas console: Sign in to the AWS Management Console for AWS Service Quotas in your source Region. Navigate to AWS services and select Amazon Bedrock. Search for Global cross-Region model inference tokens per minute for your specific model. Select the quota and choose Request increase at account level. Enter your desired quota value with justification for the increase. Submit the request for AWS review. Plan ahead when requesting quota increases to help ensure capacity is available before your launch or scaling events. For large-scale deployments or time-sensitive launches, we recommend working with your AWS account team to help ensure appropriate capacity planning and expedited review. With quota management strategies in place, let’s explore how to choose between Opus 4.6, Sonnet 4.6 and Haiku 4.5 for your specific use cases. Migrating from Claude 3.x to Claude 4.5 / 4.6 The migration from Claude 3.x to Claude 4.5 / 4.6 represents a substantial technological leap for organizations using either Opus, Sonnet or Haiku versions. Claude’s hybrid reasoning architecture introduces substantial improvements in tool integration, memory management, and context processing capabilities. For more technical implementation guidance, see the AWS blog post, Migrate from Anthropic’s Claude Sonnet 3.x to Claude Sonnet 4.x on Amazon Bedrock, which provides essential best practices that are also valid for the migration to the new Claude Sonnet 4.6 model. Additionally, Anthropic’s migration documentation offers model-specific optimization strategies and considerations for transitioning to Claude 4.5 / 4.6 models. Best practices Consider the following optimization techniques to maximize performance and minimize costs for your workloads: 1. Prompt caching for repeated context Prompt caching delivers up to 90% cost reduction on cached tokens and up to 85% latency improvement for workloads that repeatedly use the same context. Cache system prompts exceeding 500 tokens, documentation content, few-shot examples, and tool definitions. Structure prompts with static content first, followed by dynamic queries. See Prompt caching for faster model inference User Guide for implementation details. 2. Model selection strategy Consider task complexity, latency requirements, cost constraints, and accuracy needs when choosing between models. We recommend Claude Opus 4.6 for the most complex tasks requiring frontier intelligence, such as complex multi-step reasoning, sophisticated autonomous agents, and precision-critical analysis. Claude Sonnet 4.6 is well suited for complex problems requiring agent planning and execution. Claude Haiku 4.5 delivers near-frontier performance at lower cost, making it optimal for high-volume operations and latency-sensitive experiences. For multi-agent architectures, consider using Opus 4.6 or Sonnet 4.6 as orchestrator and Haiku 4.5 for parallel execution workers. 3. Adaptive and extended thinking for complex tasks Claude Opus 4.6 supports adaptive thinking, an evolution of extended thinking that gives Claude the freedom to think if and when it determines reasoning is required. You can guide how much thinking Claude allocates using the effort parameter, optimizing both performance and speed. Sonnet 4.6 and Haiku 4.5 support extended thinking, where the model generates intermediate reasoning steps through problem decomposition, self-correction, and exploring multiple solution paths. These thinking capabilities deliver accuracy improvements on complex reasoning tasks, so enable them selectively where accuracy improvements justify the additional quota usage. 4. Load testing for quota validation Run load tests before production launch to measure actual quota consumption under peak traffic. Configure your test client with adaptive retry mode (Config(retries={‘mode’: ‘adaptive’})) to handle throttling during the test, use tools like Locust or boto3 with threading to simulate concurrent requests, and monitor the CloudWatch metrics during your load test to observe TPM and RPM consumption patterns. A test with 20 concurrent threads making continuous requests will quickly reveal whether your quota allocation matches your expected load. Summary and next steps Global cross-Region inference on Amazon Bedrock delivers Claude Opus 4.6, Sonnet 4.6, and Haiku 4.5 models to organizations in Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan, and Indonesia with two key advantages: cost savings compared to Regional profiles, and intelligent routing across more than 20 AWS Regions for maximum availability and scale. This infrastructure enables production AI applications across Southeast Asia, from real-time customer service to financial analysis and autonomous coding assistants. Claude Opus 4.6 provides intelligence for the most demanding enterprise workloads, Sonnet 4.6 delivers balanced performance for daily production use cases, and Haiku 4.5 enables cost-efficient high-volume operations. For multi-agent architectures, combine these models to optimize for both quality and economics. We encourage you to get started today with Global cross-Region inference in your applications. Complete the following steps to begin: Sign in to the Amazon Bedrock console in any of the source Regions listed above, e.g. Singapore (ap-southeast-1) or Jakarta (ap-southeast-3). Configure IAM permissions using the policy template provided in this post. Make your first API call using the global inference profile ID. Implement prompt caching for cost savings on repeated context. For more information: Amazon Bedrock Documentation Cross-Region inference User Guide Amazon Bedrock pricing Anthropic Claude Documentation Get started with Amazon Bedrock About the Authors Traci Lim Traci Lim is a Senior AI/ML Specialist Technical Account Manager at AWS based in Singapore. A machine learning engineer by trade, he works with startups and enterprises to operationalize and scale AI/ML applications in production, with a focus on GenAIOps, Agentic Ops, operational excellence, and cost and performance optimization. Prior to AWS, Traci led engineering teams in the tech and financial industries, scaling distributed AI systems across AWS, Azure, GCP, and SAP. He is a builder at heart, always looking for ways to create meaningful impact through technology. Vincent Wang Vincent Wang serves as a GenAI Specialist Solutions Architect at AWS, based in Sydney, Australia. Drawing on more than 8 years of experience in cloud computing, he plays a key role in designing and consulting on modern cloud-native architectures that enable customers to harness the power of AI and machine learning for their businesses. His areas of expertise include AI, Agentic AI, and open source software. Chanmi EUN Chanmi EUN is a Senior Go-to-Market Specialist for Generative AI at Amazon Web Services in Singapore, where she drives adoption of cutting-edge AI technologies among startup customers. She crafts strategic initiatives, develops impactful sales plays, and orchestrates partnerships to accelerate generative AI adoption across the Asia-Pacific Region. Drawing on rich experience in the tech industry, Chanmi seamlessly combines deep expertise with her multilingual capabilities to deliver transformative results in the rapidly evolving AI landscape. Melanie Li Melanie Li, PhD, is a Senior Generative AI Specialist Solutions Architect at AWS based in Sydney, Australia, where her focus is on working with customers to build solutions using state-of-the-art AI/ML tools. She has been actively involved in multiple generative AI initiatives across APJ, harnessing the power of LLMs. Prior to joining AWS, Dr. Li held data science roles in the financial and retail industries. Saurabh Trikande Saurabh Trikande is a Senior Product Manager for Amazon Bedrock and Amazon SageMaker Inference. He is passionate about working with customers and partners, motivated by the goal of democratizing AI. He focuses on core challenges related to deploying complex AI applications, inference with multi-tenant models, cost optimizations, and making the deployment of generative AI models more accessible. In his spare time, Saurabh enjoys hiking, learning about innovative technologies, following TechCrunch, and spending time with his family. Sharadha Kandasubramanian Sharadha Kandasubramanian is a Senior Technical Program Manager for Amazon Bedrock. She drives cross-functional GenAI programs for Amazon Bedrock, enabling customers to grow and scale their GenAI workloads. Outside of work, she’s an avid runner and biker who loves spending time o […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 week ago
Generate structured output from LLMs with Dottxt Outlines in AWS
 This post is cowritten with Remi Louf, CEO and technical founder of Dottxt. […]
This post is cowritten with Remi Louf, CEO and technical founder of Dottxt. […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 week ago
Train CodeFu-7B with veRL and Ray on Amazon SageMaker Training jobs
 The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has created unprecedented […]
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has created unprecedented […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 week ago
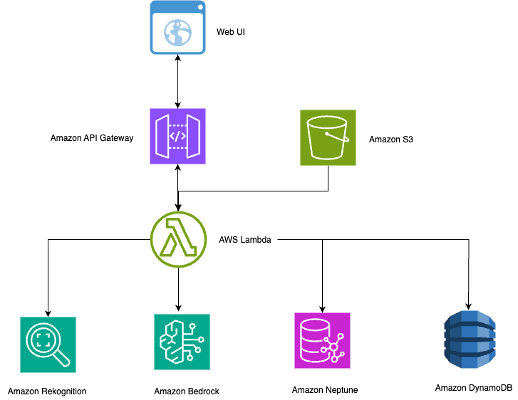
Build an intelligent photo search using Amazon Rekognition, Amazon Neptune, and Amazon Bedrock
 Managing large photo collections presents significant […]
Managing large photo collections presents significant […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 week, 1 day ago
Agentic AI with multi-model framework using Hugging Face smolagents on AWS
 This post is cowritten by Jeff Boudier, Simon Pagezy, and Florent G […]
This post is cowritten by Jeff Boudier, Simon Pagezy, and Florent G […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 week, 1 day ago
Accelerating AI model production at Hexagon with Amazon SageMaker HyperPod
 This blog post was co-authored with Johannes Maunz, Tobias Bösch […]
This blog post was co-authored with Johannes Maunz, Tobias Bösch […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 week, 1 day ago
How Sonrai uses Amazon SageMaker AI to accelerate precision medicine trials
 In precision medicine, researchers developing diagnostic tests for early […]
In precision medicine, researchers developing diagnostic tests for early […] -
AWS Machine Learning wrote a new post on the site CYBERCASEMANAGER ENTERPRISES 1 week, 1 day ago
Scaling data annotation using vision-language models to power physical AI systems
 Critical labor shortages are constraining growth across […]
Critical labor shortages are constraining growth across […] - Load More